GENERAL
Who is subject to Income Tax in India ?
Income tax is levied on all legal entities both real as well as artificial. It
is payable on total income. Different legal entities as recognised under
Income Tax Act are:
i) Individual & Hindu Undivided Family
ii) Firm (including partnerships)/AOP/BOI
iii) Company
iv) Local authority
#top
What are the Income Tax rates prevalent in India ?
Indian tax rates are now reasonable and are comparable to many developed
countries.There are basically five categories under which tax rates have been
divided :
1) Individuals (including non residents). This category also includes
H.U.F., A.O.P., etc.
INCOME |
TAX RATE |
a) upto Rs.50000 |
Nil |
b) between Rs.50001 to Rs.60000 |
10 % of the amount above Rs.50000 |
c) between Rs.60001 to Rs150000 |
Rs1000 + 20% of the amount above Rs.60000. |
d) above Rs.150000 |
Rs.19000+30% of the amount above Rs.150000. |
2) Partnership firms and domestic companies incorporated in India will
be charged at a flat rate of 35% .
3) Foreign company (as defined under Companies Act). The rate
applicable depend upon the type of Income. In case of Income pertaining to
Royalties & fees for technical services will be 50%. In all other cases, it
will be 48%.
4) Co-operative society
INCOME |
RATE |
a) upto Rs.10000 |
10% |
b) between Rs.10000 to Rs.20000 |
Rs.1000 + 20% of the amount above Rs.10000 |
c) above Rs.20000 |
Rs.3000+ 35%of the amount above Rs.20000. |
5) Local Authority will be charged at a flat rate of 30%
In case the total income is greater than Rs.60000: Calculate tax as per
the above rates, give effect to rebate u/s 88 and 88B, add 10% surcharge on
the tax so derived. The total shall be the tax payable. This does not apply to
foreign residents and foreign companies.
#top
In case of individuals how does one decide if the income is taxable to Income
Tax?
Income which is subject to tax depends on the residential status of a person.
Therefore, it is important to be able to determine the residential status
of a person. Under the Income tax there can be three types of residential
status.
a) Resident
b) Resident but not ordinarily resident
c) Non resident
#top
How do you determine the residential status (for tax purposes only) ?
Your residential status is determined based upon fulfillment of certain
conditions :
to enlarge, click on the flowchart
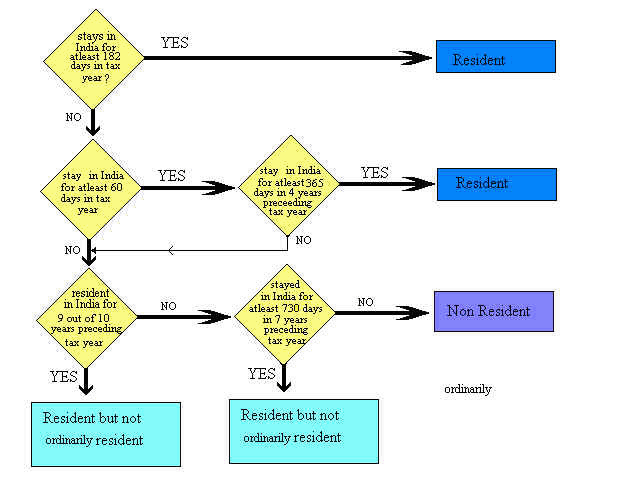
Notes :
Stay : aggregate period of total no.of days spent in India.
Tax year : 1 April to 31 March
#top
What are the consequences of being classified under different residential
status ?
A person classified as a resident will have his total income, whether
accrued/rec’d in India or anywhere else subject to Indian income tax.
A person classified as a resident but not ordinary resident will have
his total income received and accrued in India and also that income accrued
outside India which is derived from a business or profession set up in India,
subject to income tax.
A non resident will have only that part of his total income subject to
income tax which is received and accrued in India.
#top
Whether you are required to file your return of Income ?
If the total income exceeds the amount not chargeable to tax, then Income Tax
return has to be filed. For example, in case of individuals, the Income tax
return has to be filed if the total income exceeds Rs.50000. It may be noted
that any person having total income below taxable limit can also file the
return.
As part of its efforts to widen the tax base, the government has made changes
which require certain other individuals whose income is less than Rs.50000
also to file their Income Tax return.This criteria is based on economic
indicators (Popularly known as one by six ) as follows:
(a) If he occupies an immovable property exceeding floor area as specified
whether by way of ownership, tenancy or otherwise. For example,
specified floor area for Delhi &Mumbai is 600sq.ft
while for Kanpur it is 1100 sq ft. OR
(b) he has a motor vehicle (includes scooters & Motor cycles), whether owned
or leased. However, Motor cycles & scooters are exempted from next year OR
(c) he is a subscriber to a telephone OR
(d) he has during the year under consideration incurred expenditure on foreign
trip either for himself or for some other person. OR
e) he is a credit card holder. OR
f) he has a membership of a club where entrance fee is Rs.25000 or more
#top
What are the dates by which the return of income has to be filed?
Persons required to file their return of income have to do so within the
specified dates as follows :
(1) In case of an individual (not having business or profession income ) |
By 30th June |
(2) For persons other than a company :
(a) having business or profession income and not required to get his
accounts audited
(b) (i) who is required to get his accounts audited under the Income-Tax
Act or any other law
(ii) a co-operative society
(iii) for working partner of a firm whose accounts are required to be
audited under the Income-tax Act or any other law |
By 31st August
By 31st October
By 31st October
By 31st October |
(3) For a company
|
By 30th November |
#top
PERQUISITES
What does the Income Tax Act say about perquisites in general?
The Act includes perquisites in the inclusive definition of salary by virtue of
Sec 17(1). Thus perquisites are taxable as income under the head ‘Salary’.
Sec 17(2) lists certain items which are to be treated as perquisites, for
example, accomodation free of rent or at concessional rental charges, stock
options, life insurance premium, etc.
Sec 17(2) also specifies certain medical benefits which are not to be included
as perquisites.
The rules for valuation of the following perquisites are given in Rule 3 of the
Income Tax Rules:
These items are non-monetary and hence the need for laying down valuation rules.
#top
What are the valuation rules for Rent Free Accomodation?
Category A (Govt. employees) |
Category B (employees of RBI, LIC, Nationalised Banks, etc.) |
Category C (Others, i.e. non-govt. employees) |
Perquisite Value is as per Government rules |
Perquisite Value is the lesser of:
|
PV is the higher of:
10% of salary, and
Fair Rent - 40% of salary (50% in case of metropolis) |
#top
What is Fair Rent?
Fair Rent is the higher of :
However, Fair Rent cannot exceed Standard Rent
(decided in Mrs. Sheila Kaushish Vs. CIT)
#top
What is Municipal Valuation of Fair Rent?
Every municipality collects house tax based on its rental value, ie the
municipality decides what will be the rental value if the house is given on
rent. Such rental value is called Municipal Valuation of Fair Rent.
#top
What is Standard Rent?
Standard Rent is the highest possible rent of a particular property, under the
Rent Control Act.
Thus, where Rent Control Act is applicable, Standard Rent shall act as an upper
ceiling on the figure of Fair Rent.
#top
How is Salary determined for the purpose of Valuation of Rent Free Accomodation?
Three points need to be remembered in this respect.
1) Salary is taken on due basis only.
2) The following are the components of salary : Basic Pay, Dearness Allowance/
Dearness Pay (if it forms part of salary for the purpose of retirement benefits,
ie gratuity, pension, PF and leave salary), bonus, commission, fees, etc.,
taxable portion of all allowances, reimbursement of income tax and professional
tax, reimbursement of gas, electricity and water expenses, any other payment.
3) The following items are excluded from the computation of salary: value of all
perquisites, employer’s contribution to PF and interest thereon.
#top
What if the employer takes a house on rent for the employee?
While computing the value of fair rent, whether defacto rent (the rent paid by
the employer) is to be considered or not, is controversial.
a) One view is that defacto rent should be ignored as the Income Tax Rule on
valuation of rent free accomodation is silent about it.
b) The second view equates defacto rent to fair rent.
c) The third view takes defacto rent into consideration for calculating fair
rent. As per this view, if defacto rent exceeds the fair rent calculated
otherwise (i.e, upto the step in which Standard Rent is considered), then
defacto rent shall be taken to be the Fair Rent.
#top
What if the Rent Free Accomodation is a furnished one?
In this case, first the value of rent free accomodation is calculated assuming
it is not furnished. If the furnishing is owned by the employer, 10% of the
original cost of furnishing is added; and if the furnishing is taken on hire,
the actual hire charges are added.
#top
What are the valuation rules for Accomodation provided at concessional rates?
First, the perquisite value is calculated assuming the accomodation is provided
rent free. From this value, the rent for the period of occupation payable by the
employee to the employer is deducted. This gives the perquisite value for
accomodation provided at concessional rates.
#top
Is the Motor Car facility treated as a perquisite for all types of employees?
No, a motor car provided to employees shall be treated as a perquisite only in
the case of ‘specified employees’.
However, if the car is owned by the employee and the employer merely bears the
expenses on the car, then the perquisite value shall be computed even if the
employee is not a specified employee.
#top
Who is a ‘specified employee’?
A ‘Specified employee’ is the one who satisfies any of the following cases:
he is a director of the company,
he has a substantial interest in the company, ie he is the beneficial owner of
equity shares carrying 20% of voting power in the employer company.
his monetary income under the head "Salaries" for the year exceeds
Rs.24,000. The amount considered here includes amounts due from, paid or
allowed by one or more employers. It excludes all non-monetary benefits. Also,
deductions in respect of monetary payments exempt from income tax, standard
deduction, deduction for educational allowance and deduction on account of
professional tax will be allowed for this purpose.
#top
How is the value of Motor Car facility computed?
The following table gives the perquisite value of the motor car facility under
different situations, taking the written down value of the car at the beginning
of the year as Rs.2,00,000, depreciation u/s 32 of the Income Tax Act at 20%, ie
Rs.40000 and expenses on the car during the year Rs.50,000.
Use of Car |
Car owned by Employer |
Car owned by Employee |
|
Expenditure by Employer |
Expenditure by Employee |
Expenditure by Employer |
Exp. by Employee |
Official |
Nil |
Nil |
Nil |
Nil |
Personal |
Depreciation of car + Expenses borne by Employer
40000+50000 |
Depreciation of car
40000 |
Expenses borne by Employer
50000 |
Nil |
Official & Personal, segregation is possible
(lets say 60% official and 40% personal) |
Personal share in :
Depr. of car + exps. borne by employer
40%*(40000+50000) |
Personal share in :
Depr of car
40%*(40000) |
Personal share in :
Exps borne by employer
40%*(50000) |
Nil |
Official & Personal, segregation is not possible. |
Till 16 hp: Rs.600 p.m.
More than 16 hp: Rs.800 p.m.
If driver is provided, Rs.300 p.m. shall be added |
Till 16 hp: Rs.200 p.m.
More than 16 hp: Rs.300 p.m. |
Reasonable Perquisite value as decided by the Assessing Officer. |
Nil |
16 hp (horsepower) = 1880 cc
The above is based on the following logic:
PV = Nil if the car is used only for official purposes, whoever be the owner
and whoever bears the expenses. There is no personal use involved and so there
is no perquisite.
PV = Nil if the employee owns the car and also incurs all expenses on the car,
whatever be the use. As the employer is in no way concerned with the car,
there is no perquisite.
If the car is owned by the employer and there is personal use, then PV will
include the entire or a certain proportion of depreciation on the car.
If the expenses are borne by the employer and there is personal use, then PV
will include all or a certain proportion of those expenses.
#top
What happens in case the employer maintains a pool of cars?
If the employer has provided a number of cars of different horse powers to a
number of employees, for personal as well as official uses, it will be presumed
that every employee was using the car with the highest horsepower rating and the
perquisite value will be computed accordingly.
Similarly, if there are some cars without driver and some with driver, it will
be presumed that every employee was using the car with driver.
#top
What if the employee pays certain amount for using the car?
If the employee is paying a certain amount for using the car, such payment shall
be deducted from the perquisite value.
#top
What if the employee uses the official car only to commute between office and
residence?
Such use shall be treated as official use and hence there is no perquisite.
#top
Is the gas / electricity / water facility a perquisite for all employees?
If the facility for gas/ electricity/ water is provided by the employer, then
the perquisite value shall be computed only in the hands of
specified employees.
If the connection is in the name of the employee and the employer merely bears
the expenses, perquisite value shall be computed even if the employee is not a
specified employee.
#top
How is the perquisite value computed for gas/ electricity/ water facility
provided by the employer?
If the facility is provided by the employer, it shall be a perquisite only in
the hands of specified employees.
If the employer supplies these from his own sources, PV = Nil
If the facility is purchased by the employer and the employee uses it only for
personal purposes, PV = the amount spent by the employer.
If the facility is purchased by the employer and is used by the employee for
both official and personal purposes, then PV is taken as 6.25% of salary but
shall not exceed the amount actually spent by the employer. Salary for this
purpose shall be:
Basic pay on due basis
Dearness Allowance or dearness pay, if the terms of employment so provide
Commission, if it is on sales turnover, calculated at a fixed rate and the
employee works in the sales department.
#top
What if the gas/ electricity/ water connection is in the name of the employee
and the employer bears the expenses?
This is a case of reimbursement of employee’s expenses. All employees shall be
covered, whether or not they are specified employees. The entire amount borne by
the employer shall be taken to be the perquisite value.
#top
What are the rules for computing perquisite value of Free Education provided by
the employer?
Free Education provided by the employer is a perquisite only for
specified employees.
If the employer provides free education to employee, PV = Nil.
If the employer provides free education to the family members of the employee,
PV = actual amount spent by the employer.
If free education is provided in an instition run by the employer himself, PV =
cost of education in a similar institution in the same locality.
If any scholarship is given to the family members of the employee purely on the
basis of merit, PV = nil.
#top
What if the employee’s costs on education are borne by the employer?
The entire amount borne by the employer shall be the perquisite value. This
shall be applicable in the cases of all employees, not just the specified
employees.
#top
What are the valuation rules for transport facility provided by a transport
undertaking free of cost or at concessional rates?
Nil.
Various organisations running transport services provide free or concessional
travel to their employees/ their family members/ dependent relatives in
conveyance owned by the undertaking. The perquisite value of such benefit shall
be taken to be nil.
#top
How to value a perquisite for which no specific rules are given in Rule 3 of the
Income Tax Rules?
The
valuation will be done in a way the Assessing Officer considers fair and
reasonable.
#top
How is the perquisite value determined in case a watchman / sweeper / gardener /
other domestic servant is hired by the employee and the expense is borne by the
employer?
The
actual expense borne by the employer shall be taken to be the perquisite value.
This shall apply to all categories of employees, not just the specified
employees.
#top
What if the servant is hired by the employer and his services provided to the
employee?
In
this case, perquisite shall be only in the hands of
specified employees.
The
Perquisite Value in the case of watchman, sweeper and gardener shall be Rs.120
per month per person. For other domestic servant, the PV shall be actual wages
paid by the employer.
Special Case:
If
accomodation owned by the employer is provided to the employee and a gardener is
provided alongwith the accomodation, then there shall be no separate perquisite
value for the gardener; the gardener’s actual salary shall be added to
the Fair Rent of the accomodation. (CBDT Circular 122)
top
|